EPC Gets Granular: Motor Drive Reference Design Targets Robotic Joints
EPC recently announced a new reference design for BLDC motor drives to provide intricate motor control in humanoid robots.
It seems unreal that workers may one day work alongside humanoid robots from companies like Boston Dynamics or Rainbow Robotics. While these robots still have a long way to go, Efficient Power Conversion (EPC) is supporting this manufacturing dream with a new reference design.
.jpg)
The EPC91104’s compact design allows the evaluation board to be placed closer to the finger and wrist joints.
EPC created the new GaN-based motor drive reference design to support precise motion in humanoid robots, particularly for wrist, finger, and toe joints.
Finer Motor Control and Precision
The EPC91104 evaluation board is a high-performance, three-phase brushless DC motor drive inverter designed to power compact, high-precision motors in humanoid robots. The board uses the EPC23104 ePower Stage IC (datasheet linked) featuring a maximum RDS(on) of 11 mΩ and supports DC bus voltages of up to 80 V.
It operates effectively with a wide voltage range from 14 V to 80 V, accommodating diverse battery systems. A steady-state output current capability of 14 Apk and pulsed current of 20 Apk allows the board to meet the demanding requirements of precision motion in humanoid robotics. The EPC23104 also features a low-distortion switching technology that reduces motor noise and torque ripple.
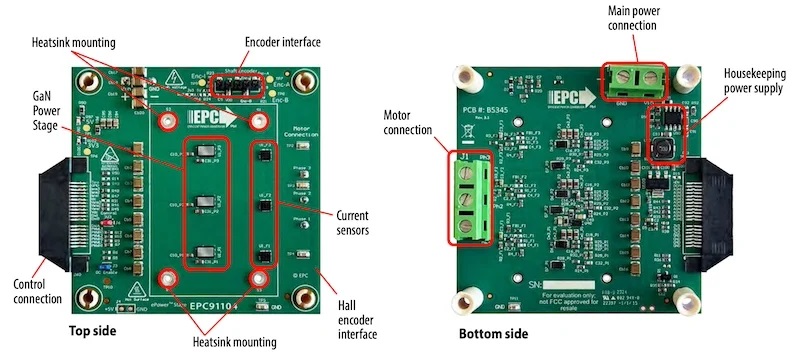
The main sections of the e EPC91104 board.
The EPC91104 includes essential protective features such as overcurrent and input under-voltage protection, ensuring stable operation even in challenging environments. Its compact design allows manufacturers to place it in space-constrained applications—I mean, how much room do you have around your pinky toe? Additionally, the board is compatible with various leading controller manufacturers, providing developers the flexibility for efficient prototyping and integration.
Wrists, Elbows, Knees, and Toes
For those seeking higher power solutions, EPC also offers the EPC9176, another design that caters more to applications that require more robust current handling, such as elbow and knee motors in humanoid robots.
The EPC9176 is a three-phase BLDC motor drive inverter board using the EPC23102 ePower Stage IC (datasheet linked) with a maximum RDS(on) of 6.6 mΩ and 100 V device voltage. It delivers up to 35 Apk (25 ARMS) steady state and 40 Apk pulsed output current. The board includes essential functions for a complete motor drive inverter, such as gate drivers, regulated auxiliary power, voltage and temperature sensing, accurate current sensing, and protection features.
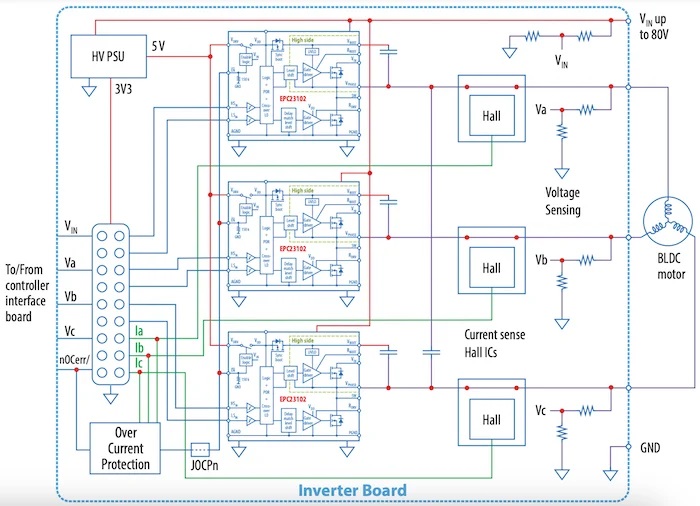
Block diagram of EPC9176 board for a BLDC drive.
It seems plausible that you or someone you know might be working shoulder-to-shoulder with a humanoid robot in the next few years. Indeed, the robotics for such a goal is still lacking in the more intricate work, such as running a wiring harness on a Tesla assembly line. However, with the development of finer motion control, provided by solutions like the EPC91104 and the EPC9176, humanoid robots may become more adept at achieving these intricate tasks.



